CUTANEOUS LEUKOCYTOCLASTIC VASCULITIS INDUCED BY PROPYLTHIOURACIL
Abstract
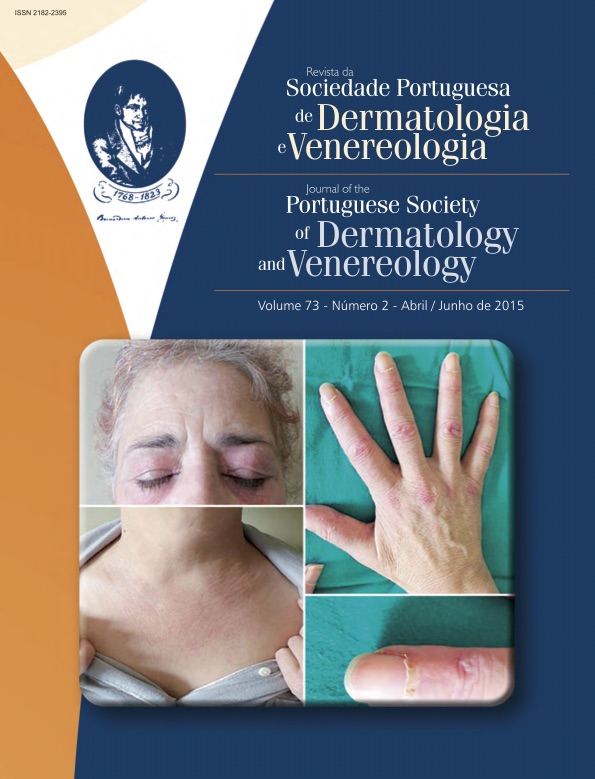
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is widely used in the treatment of Hyperthyroidism. Usually well tolerated, it is though associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) and, less frequently, with late-onset ANCA positive vasculitis. The authors describe the clinical case of a 45-year-old female patient with Graves’ disease for which she was being treated with PTU since 3 years before, who developed an ANCA-positive cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis without systemic involvement. Initially seen as idiopathic the vasculitis was posteriorly associated with PTU. The drug was discontinued with a progressive and maintained recovery. The patient remains asymptomatic with 3 years of follow-up.
Downloads
All articles in this journal are Open Access under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0).